How to Start Foraging Mushrooms Without Dying or Accidentally Tripping
“], “filter”: { “nextExceptions”: “img, blockquote, div”, “nextContainsExceptions”: “img, blockquote”} }”>
Wild mushrooms make a great addition to any backcountry meal, and if you know how to look, you can find them along your local forest trails. Start foraging with these tips from Beck Ferguson, professional mushroom hunter, grower, and owner of central Vermont’s Mansfield Mushroom Co.
Editor’s note: Eating any mushroom you can’t positively identify is a very bad idea. While these five species are among the easier to identify and don’t have many deadly lookalikes, make certain by taking a class or double-checking your finds with a more experienced friend.
(Photo: Ivan Marjanovic via Getty Images)
Chicken of the Woods
When: Spring into fall
Where: At the bases and on the trunks dead, dying, and living hardwood trees
This porous, shelf-like mushroom stands out like, well, a chicken in the woods: Its clusters of bright orange and yellow can grow heavier than 50 pounds. When cooked properly, it often has a similar taste and texture to its eponymous poultry.
 (Photo: laigor via Getty Images)
(Photo: laigor via Getty Images)
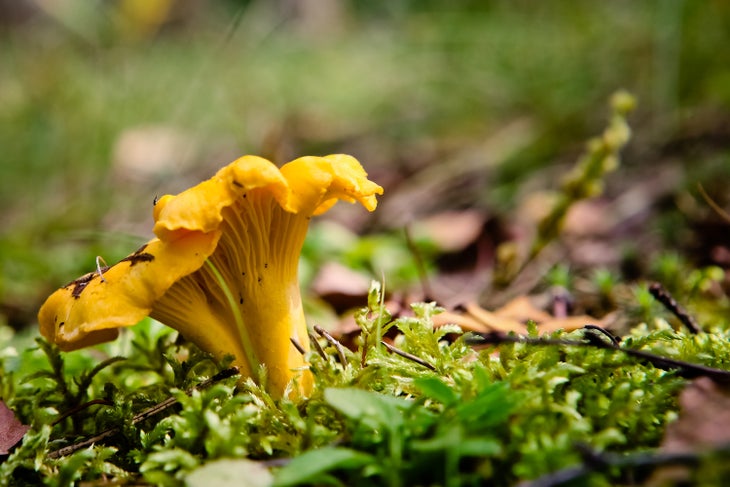
Golden Chanterelle
When: Early summer into fall
Where: On forest floors near living hardwood trees
This burst of sunshine is a great source of beta-carotene, hence its golden hue. It also has a flowery fragrance and apricot-like flavor. You can identify it from the wrinkles running down the stem from under the cap.
 (Photo: Karel Bock via Getty Images)
(Photo: Karel Bock via Getty Images)
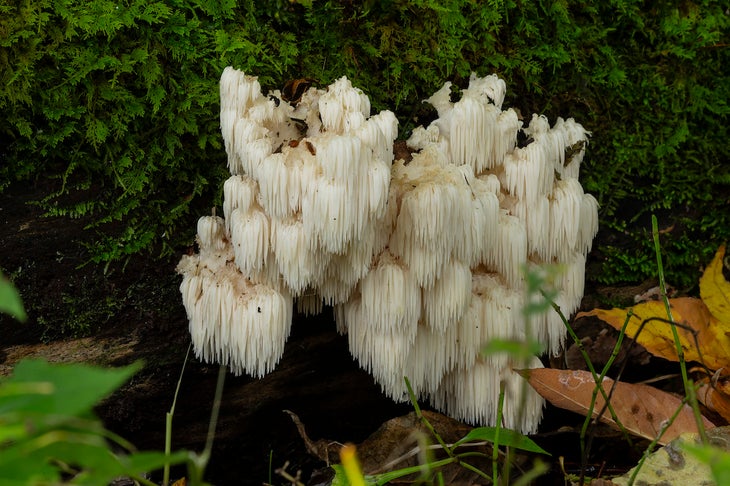
Lion’s Mane
When: Summer into fall
Where: In the abscesses of dead or dying hardwood trees
If you see Cousin Itt’s fungus relative growing on a tree, you’ve found a lion’s mane. This mushroom stands out for its mop of tiny, hairlike teeth (as opposed to pores or gills). When cooked, it has a texture similar to shellfish, like crab and lobster, and as a bonus, it strengthens your immune system.
 (Photo: crotography via Getty Images)
(Photo: crotography via Getty Images)
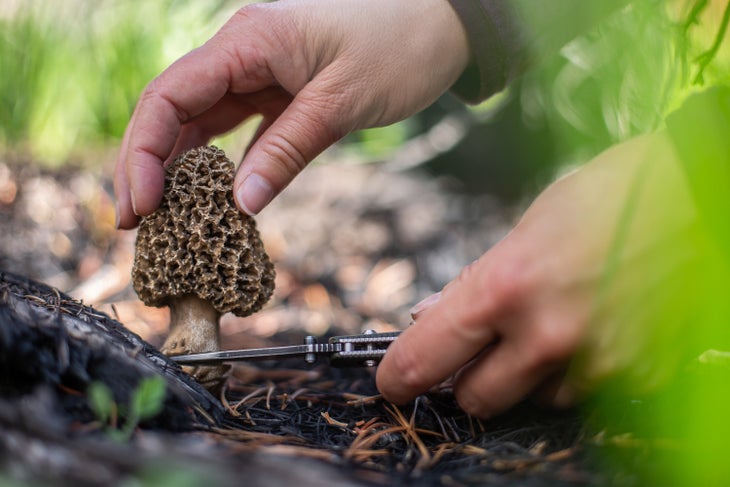
Morel
When: Jump
Where: Around the bases of dead or dying oak, elm, ash, and aspen trees
Morels are prized for their meaty flavor and easy identification. When you spot a morel, be sure to verify that your find isn’t a potentially poisonous lookalike: A true morel is completely hollow, and a false morel has inward-growing folds chambered inside.
 (Photo: Erik Agar via Getty Images)
(Photo: Erik Agar via Getty Images)
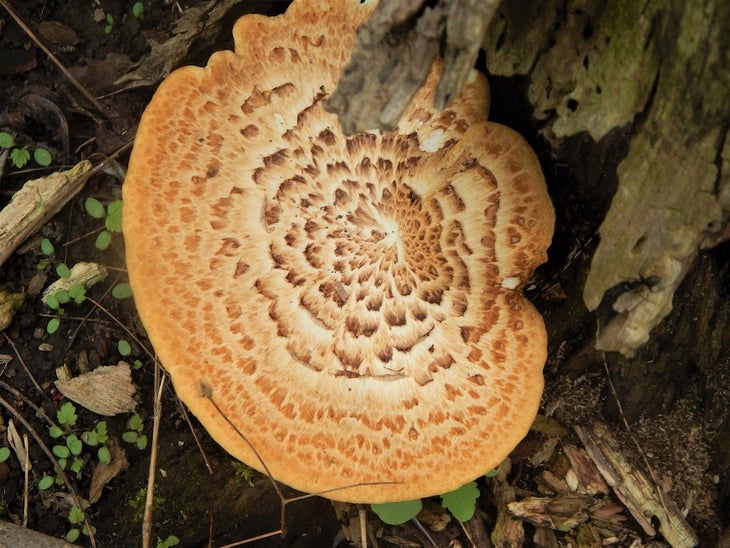
Pheasant Back (aka Dryad’s Saddle)
When: Jump
Where: On dead or dying hardwood trees, particularly elms or oaks, and living maple trees
Whatever you call this mushroom, its name is very fitting: In Greek mythology, a dryad is a spirit that lives in the trees, and the pattern on the cream-colored, shelf-like cap is akin to the feathers on a pheasant’s back. When young, this mushroom’s taste is reminiscent of fresh watermelon or cucumber.


Comments are closed.